[Editor’s note]
The 48-episode TV series "Deng Xiaoping at a turning point in history" was officially launched on CCTV 1 on August 8, which triggered a heated discussion among netizens. The drama broadcast that day involved the plot of smashing the Gang of Four. The Paper specially excerpted the relevant contents about this matter in the book History of communist party in China.
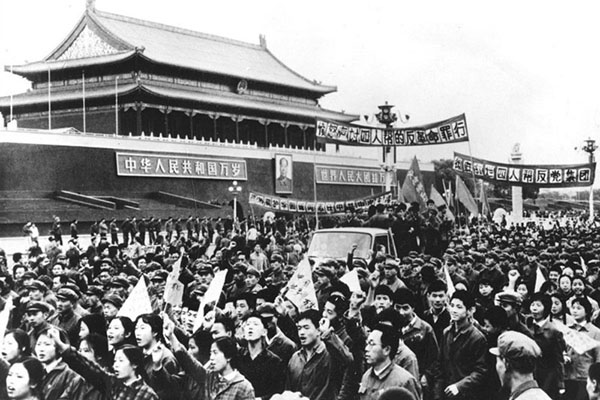

In October 1976, people from all walks of life in the capital gathered and marched, cheering and smashing the victory of the Gang of Four.
Hua Guofeng was aware of the danger of the Gang of Four usurping the Party.
After the death of Mao Zedong, the Gang of Four stepped up their conspiracy to seize the supreme leadership of the Party and the state. While Mao Zedong was seriously ill, in late August, the gang of four’s best friend in Shanghai suddenly distributed weapons and stepped up the equipment of Shanghai militia, firing 74,220 guns, 300 guns and more than 10 million rounds of various ammunition in an attempt to make Shanghai a base for them to seize the highest power. After Mao Zedong’s death, their conspiracy became even more unbridled. On September 11th, Wang Hongwen set up another duty room in Zhongnanhai instead of the duty room of the Central Office, and informed the party committees of all provinces, municipalities and autonomous regions that major issues should be reported to them in a timely manner in an attempt to cut off the contact between the CPC Central Committee and all localities and command the whole country by them. Jiang Qing tried her best to master the documents and materials kept by Mao Zedong. The Gang of Four also monitored Hua Guofeng’s actions. They secretly made many arrangements for Shanghai’s cronies. The Gang of Four manipulated some people in Tsinghua University, Peking University, Xinhua and other units to write "loyalty letters" and "persuasion letters" to Jiang Qing. Some people openly asked Jiang Qing to "serve as Chairman the Central Committee of the Communist Party of China and Chairman of the Military Commission" and "shoulder this heavy burden". Wang Hongwen made a standard portrait ready to be hung in the whole country, and ordered the literary and art circles to shoot films such as "Grand Festival".
As the first vice-chairman of the CPC Central Committee and presiding over the work of the Central Committee, Hua Guofeng was aware of the serious danger of the Gang of Four usurping the party and seizing power, and thought that it was necessary to urgently seek countermeasures to remove this gangrene from the body of the party and the state. On September 11th, Hua Guofeng went to Li Xiannian’s residence and said: The struggle against the Gang of Four is inevitable, and now it’s time to solve it. Hua Guofeng also asked Li Xiannian to go to see Ye Jianying on his behalf and ask Ye Jianying for advice on how and when to solve the problem of the Gang of Four. On September 14th, Li Xiannian went to Ye Jianying’s residence, conveyed Hua Guofeng’s opinion and studied the matter with him. After repeated studies with Ye Jianying, Li Xiannian and Wang Dongxing, Hua Guofeng thought that the struggle against the Gang of Four was deadly and beyond the scope of normal inner-party contradictions and struggles, and decisive measures should be taken to solve them, but it was also necessary to avoid causing major social unrest.
People’s Daily published forged dying entrustment.
In order to create public opinion for coming to power, the Gang of Four forged a so-called dying order from Chairman Mao, which was "to follow the established policy". On September 16th, People’s Daily, Red Flag magazine and People’s Liberation Army Daily published editorials saying: "Chairman Mao enjoined us to’ follow the established policy’." "To follow the established policy is to follow Chairman Mao’s proletarian revolutionary line and various policies." They took "following the established policy" as the propaganda center at that time, occupied the main page in newspapers and periodicals, repeatedly publicized, raised themselves and attacked Hua Guofeng and others.
The Gang of Four forged Mao Zedong’s dying "orders", which aroused Hua Guofeng’s greater vigilance. Compared with the three sentences written by Mao Zedong more than four months ago, on October 2, Hua Guofeng corrected this formulation in the "Speech by the Head of the China Delegation at the 31st Session of the United Nations General Assembly" submitted for review, and instructed: I checked it correctly, and I made three mistakes with Chairman Mao’s handwriting. What Chairman Mao wrote and what I conveyed to the Politburo were "to follow the past policy". In order to avoid further misinformation, I deleted it. However, Zhang Chunqiao instructed in this document: "The proposal will not be issued." Jiang Qing agrees with Zhang Chunqiao. On the one hand, the Gang of Four blocked the issuance of Hua Guofeng’s instructions to prevent the fraud of forging Mao Zedong’s dying "instructions" from being exposed; on the other hand, they instructed their writing team to concoct another article with a higher tone of "following the established policy". On October 4th, Guangming Daily published "Liang Xiao" article "Always Follow Chairman Mao’s established policy". The article said: "To tamper with Chairman Mao’s established policy is to betray Marxism, socialism and the great theory of continuing revolution under the dictatorship of the proletariat." "Any revisionist leader who dares to tamper with Chairman Mao’s established policy will definitely come to no good end." The article is directed at leaders such as Hua Guofeng who presided over the central work.
Around this time, the activities of the Gang of Four conspiring to usurp power were even more explicit. On October 1st, Jiang Qing made a speech in Tsinghua University, warning everyone: "There will be someone who will reverse his conviction for him", and said: "I also want to swear to you young people that you must exercise well and fight with them. Class struggle and line struggle are still long." On October 3rd, when Wang Hongwen spoke in Pinggu County, Beijing, he declared: "The Central Committee has revisionism. What will you do? Down! " "There may be Tang Xiaoping, Wang Xiaoping and the like in the future, so be alert!" "Look at revisionism with your eyes wide open."
The older generation of revolutionaries turned the crisis around
Ye Jianying, Li Xiannian and many other revolutionaries of the older generation were deeply worried by the activities of the Gang of Four to usurp the party and seize power. Most of them are in a difficult situation, but they still exchange information through various channels and forms, put forward suggestions to reverse the crisis, and brew solutions to the problem of the Gang of Four. Hua Guofeng, Ye Jianying, Li Xiannian, Wang Dongxing and others, after careful consideration and repeated discussions, and with the consent of most comrades in the Political Bureau of the Central Committee, decided to take measures to isolate and censor the Gang of Four.
At 8 pm on October 6, Hua Guofeng and Ye Jianying convened a The Politburo Standing Committee (PSC) meeting in Huairentang, Zhongnanhai, and informed Yao Wenyuan to attend. When Zhang Chunqiao, Wang Hongwen and Yao Wenyuan arrived in the conference room successively, they announced that they would be quarantined for review. At the same time, send someone to Zhongnanhai Jiang Qing’s residence to announce the implementation of the same decision. The evil gang of four was smashed in one fell swoop. At the same time, the Party Central Committee sent people to take over the central propaganda organizations controlled by the Gang of Four, such as Xinhua News Agency, china national radio and People’s Daily. At 10 o’clock that night, the Central Committee of the Communist Party of China held an emergency meeting of the Political Bureau, decided to smash the major issues of the party and the country after the Gang of Four, and unanimously passed the resolution that Hua Guofeng was appointed as Chairman of the Central Committee of the Communist Party of China and Chairman of the Central Military Commission (to be ratified by the Third Plenary Session of the Tenth Central Committee of the Party).
From October 7 to 14, the Political Bureau of the Central Committee held a greeting meeting in batches in Beijing attended by the central party, government and military organs, the heads of provinces, autonomous regions, municipalities directly under the Central Government and major military regions, and reported the decisive measures taken against the Gang of Four and the resolution of the CPC Central Committee on Hua Guofeng’s appointment as Chairman of the Central Committee of the Communist Party of China and Chairman of the Central Military Commission. The meeting exposed the conspiracy and crimes of the Gang of Four to usurp the party and seize power, arranged the important work of the party and the state after the downfall of the Gang of Four, and determined the policy of both solving problems and stabilizing the situation. On October 8th, the Central Committee of the Communist Party of China made two decisions: First, establish a memorial hall for President Mao Zedong in Beijing, and move the crystal coffin containing Mao Zedong’s body into the hall, so that the masses can pay tribute to his remains. Second, publish the fifth volume of Selected Works of Mao Zedong as soon as possible, and prepare for the publication of The Complete Works of Mao Zedong.
Disintegrate the armed rebellion in Shanghai in advance
After the backbone of the Gang of Four in Shanghai found out that Jiang Qing and others had been quarantined and censored, they immediately mobilized urgently in an attempt to launch an armed rebellion. They organized the command team, mobilized the militia, used a variety of guns and vehicles, concentrated a lot of materials and food, and deployed specific steps of armed rebellion, preparing for a final struggle to save Jiang Qing’s counter-revolutionary group. They are also going to publish a letter to the people of the whole city, and put forward slogans such as "Give me back Jiang Qing, give me back the Spring Bridge, give me back Wen Yuan and give me back Hong Wen". The Central Committee of the Communist Party of China anticipated the problems in Shanghai and took effective measures in time to control the situation in Shanghai. The plot of Jiang Qing’s counter-revolutionary group to launch an armed coup collapsed in an instant. After the plot of Jiang Qing’s counter-revolutionary group to instigate an armed coup in Shanghai was shattered, the people of Shanghai denounced the Gang of Four and swept the city.
On October 18th, the Central Committee of the Communist Party of China issued the "Notice on Wang Hongwen, Zhang Chunqiao, Jiang Qing and Yao Wenyuan’s Anti-Party Group Events" to the county-level party organizations, informing them of the crimes of the Gang of Four and Mao Zedong’s criticism of them since February 1974, calling on the whole party to unite closely and launch a struggle to expose and criticize the Gang of Four, and hoping that comrades who made mistakes, including serious mistakes, would wake up as soon as possible. The "Notice" also emphasizes: in the struggle, we should pay attention to policies, expand the scope of education, narrow the scope of attack, and treat people who make mistakes differently; The struggle against the Gang of Four is always carried out under the leadership of Party committees, and effective measures should be taken to eliminate factionalism.
“举国上下一片欢腾”
粉碎“四人帮”的消息一经公开,全国各族人民欣喜若狂,举国上下一片欢腾。从10月21日至30日,全国29个省、市、自治区和人民解放军各部队举行盛大集会和游行,拥护党中央粉碎“四人帮”的果断措施,庆祝粉碎“四人帮”的重大胜利。工人、农民、解放军和学生代表纷纷发言,称颂粉碎“四人帮”是为党锄奸,为国除害,为民平愤。21日,首都北京150万军民举行声势浩大的庆祝游行。从清晨开始,一队又一队各界群众高举红旗,敲锣打鼓,从四面八方涌向天安门广场。天安门广场上红旗如林,歌声、锣鼓声、鞭炮声、口号声响成一片。人们载歌载舞,开怀畅饮,很多大中城市的烟花爆竹销售一空,大小商店的酒柜前排起了长队。有30多个国家和地区的电视台收录并播放了首都百万群众在天安门广场举行庆祝大会的实况。香港、澳门各界爱国同胞也举行了庆祝集会。关心祖国命运的海外华侨欢欣鼓舞,表示“心中的一块石头落了地”。
Crushing Jiang Qing’s counter-revolutionary clique is a struggle carried out by the Political Bureau of the Central Committee in a special way under the extraordinary situation by carrying out the will of the Party and the people. This is a great victory achieved by the long-term struggle of the whole party, the whole army and the people of all ethnic groups throughout the country. Hua Guofeng, Ye Jianying and Li Xiannian played an important role in the struggle to crush Jiang Qing’s counter-revolutionary clique. The crushing of Jiang Qing’s counter-revolutionary clique realized the common will of the Party and the people, saved the Party, the country and the socialist cause in China from the crisis, and created the premise for realizing the great turning point of the Party’s history.
Jiang Qing and others pushed the "Left" mistakes to extremes in the "Cultural Revolution" and committed countless crimes. From November 1980 to January 1981, Lin Biao and Jiang Qing, two counter-revolutionary groups that caused disasters to our country and nation during the "Cultural Revolution", were prosecuted by the the Supreme People’s Procuratorate Special Prosecutor’s Office and tried in public by the the Supreme People’s Court Special Court. The trial of two counter-revolutionary groups, Lin Biao and Jiang Qing, according to law is of great significance for the political life of the party and the country to turn into the legal track, and has achieved a historic turning point in restoring and rebuilding China’s judicial system.(History Research Office of the Central Committee of the Communist Party of China: History of communist party, Volume II (1949-1978), History of the Communist Party of China Press, January 2011)