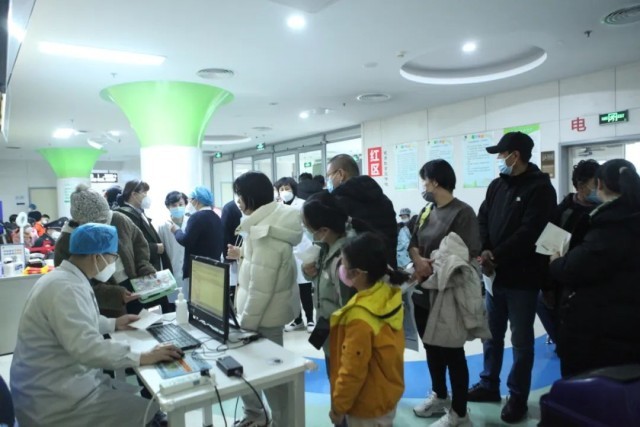
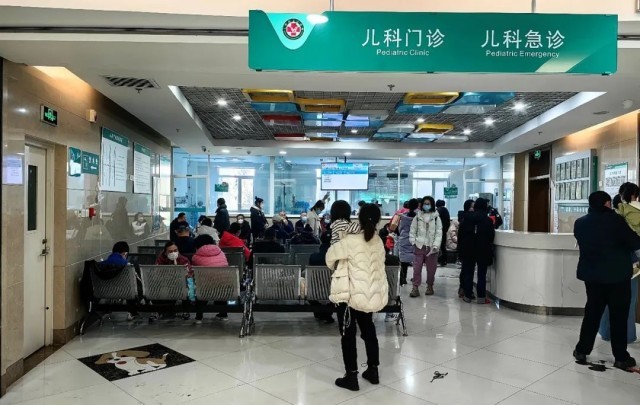
At the press conference held on November 26th, Mi Feng, spokesman of the National Health and Wellness Commission, said that monitoring showed that influenza was the main respiratory infectious disease in China recently. In addition, rhinovirus, mycoplasma pneumoniae, respiratory syncytial virus, adenovirus and other pathogens caused it.
"Influenza, respiratory syncytial virus, adenovirus, mycoplasma pneumoniae and rhinovirus are all known viruses or bacteria, and humans have coexisted with them for thousands of years." Jin Dongyan, a microbiologist and professor at Li Ka-shing Medical College of HKU, said in an interview with The Paper that people are very familiar with the characteristics of these pathogens, and most of them are self-limited diseases. A considerable number of healthy adults are immune to these pathogens, and there are no signs of super-large-scale outbreaks or significantly enhanced pathogenicity.
Lu Mengji, a German virologist of Chinese descent, also told The Paper that it is understandable that respiratory infections have increased after the management of the epidemic was lifted. In the first half of this year, children’s hospitals in Germany were also overcrowded. In his view, as the temperature drops, the pressure on hospitals in southern China may also increase, and it is suggested to protect vulnerable people through vaccination.
Jin Dongyan believes that the susceptible groups of the above pathogens are mainly the elderly and children. At present, it is necessary to nip in the bud. "Keep an eye on schools and kindergartens, find out early when there are small-scale cluster infections, and take decisive measures to effectively level the epidemic curve, reduce the total number of infected people, and at the same time reduce the pressure on medical institutions." In addition, the family should pay attention to the elderly with low immunity. "Children are sick, so we should pay attention to isolating the elderly." He suggested vaccinating the elderly and paying special attention to the elderly in nursing homes.
Previous public information showed that the number of patients in many children’s hospitals in Beijing was running at a high level and even overloaded. At the press conference on the 26th, Mi Feng suggested that large hospitals are crowded, with long waiting time and high risk of cross-infection. If there are children with mild symptoms at home, it is recommended to go to primary health care institutions or general hospitals for pediatric treatment.
Jin Dongyan also advocated that people should not gather in large hospitals for treatment. Gathering children is not only easy to cross-infect, but also may lead to the failure of timely treatment of critically ill patients.
In Jin Dongyan’s view, most of these pathogen infections are symptomatic treatment. It is not necessary to detect and determine the pathogen before treatment. "The most advanced areas in the world can’t do this." At present, only large hospitals in China can complete testing, and most primary hospitals can’t. "Time is the most important thing", if we wait for the test and then treat it, it may delay the treatment and cause the resources of large hospitals to be squeezed.
At the aforementioned press conference, Mi Feng said that all localities should scientifically coordinate medical resources, implement a graded diagnosis and treatment system, adjust their strength across disciplines and hospitals, give play to the role of medical associations, and improve the diagnosis and treatment ability of general infections and the efficiency of severe identification and referral; It is necessary to do a good job in epidemic prevention and control in key crowded places such as schools, child care institutions and nursing homes, and reduce the flow of personnel and visits. He reminded everyone that it is necessary to adhere to the sanitary habits of wearing masks, ventilation and washing hands frequently, and advocate key groups such as "one old and one small" to actively vaccinate relevant vaccines. When you have respiratory symptoms, you should be well protected, keep a social distance, and avoid cross-infection in your family and unit.
[The following is a conversation between The Paper and Jin Dongyan]
"These diseases are not difficult to treat, and they are not so special."
The Paper:In your opinion, is the main pathogen prevalent in recent respiratory infections new?
Jin Dongyan:The current situation is not consistent with the epidemic characteristics of new pathogens. First of all, there is no evidence that there is a new virus in the information released by the CDC and the Health and Health Commission. Judging from a professional point of view, if a pathogen mainly infects children, it is basically a known or past epidemic virus or bacteria. Because adults have been infected before and have immunity, adults can’t be infected or the symptoms of infection are mild or even completely asymptomatic, while children have never been exposed to this pathogen before and have no immunity, so the number of children infected is large and the impact is relatively large. Fortunately, children are infected with these pathogens, and most of the symptoms are not serious.
The Paper:Wang Quanyi, deputy director of Beijing CDC and chief expert of epidemiology, said in an interview recently that according to the latest monitoring data, the epidemic intensity of mycoplasma pneumoniae dropped to the fourth place, with the top three being influenza, adenovirus and respiratory syncytial virus.
Jin Dongyan:According to the data released by China CDC, the northern part of China is on the rise of seasonal influenza, which has not reached the peak yet, and should gradually reach the peak in the next few weeks. The South is just beginning to take the lead, while Hong Kong is over, which is below the baseline level.
All the four pathogens are known viruses or bacteria, and their epidemic characteristics, severity and severity ratio are also known. Humans have lived with them for thousands of years, so we can say that we know the root of them. We have never had a devastating epidemic in the past, and there is no sign that this will happen this year. This is a basic judgment.
About half of people are immune to Mycoplasma pneumoniae, and its infectivity is not so strong-it is usually transmitted in a crowded or closed environment after very close contact, such as eating and drinking together. Its basic reproductive rate is only 1.7, which is much lower than that of Omikjon strain in Covid-19.
From the point of view of public health, the disease control department mainly needs to deal with the cluster epidemic to prevent its scale from expanding, and if the intensity is achieved, many outbreaks can be reduced.
The Paper:Which age group are the susceptible people of these four pathogens? Is there any difference in clinical manifestations after infection, and what damage will it cause to the body if it is serious?
Jin Dongyan:Almost all susceptible people are children and the elderly.
There is little difference in clinical manifestations. In terms of drug treatment, influenza has specific drugs, such as Tamiflu and oseltamivir. There is no specific medicine for respiratory syncytial virus, adenovirus or rhinovirus. Mycoplasma pneumoniae can use azithromycin and other antibiotics. However, most influenza patients do not need to use Tamiflu or oseltamivir, and most children infected with mycoplasma pneumoniae do not need azithromycin. Patients who only have symptoms of upper respiratory tract infection and have been in good health in the past generally do not need to take antibiotics. Not all patients with mycoplasma pneumoniae positive must use antibiotics. Even in hospitals that have the conditions for testing, antibiotics are not needed for those infected with mild symptoms.
Of course, after using antibiotics, the number of bacteria in droplets decreases, which can reduce the spread. Whether to use antibiotics or not is a clinical judgment made by the attending doctor. As long as the doctor judges that the patient has or will have a high possibility of mycoplasma pneumonia, even if there is no pathogen test result, the drug should be given on a trial basis, and then whether the patient has a fever for 48 to 72 hours should be observed. If the fever has gone down, you should use it correctly, and if it hasn’t, you should change your tactics. This is the treatment procedure for mycoplasma pneumonia and other community-acquired pneumonia. This judgment should be made by a professional doctor in combination with clinical symptoms and the presence or absence of basic diseases (such as asthma).
In fact, children’s hospitals, general hospitals, pediatrics or community hospitals without pediatrics can make correct judgments as long as they are adequately trained pediatricians or general practitioners. Parents with medical knowledge can of course make their own judgments and make wise choices for their children whether and how to seek medical treatment.
Most people infected with mycoplasma pneumoniae are asymptomatic or mild, and only 3%-10% of infected people will have pneumonia. Most infected people with pneumonia are mild, and their prognosis is good. It should also be made clear to everyone that not everyone will be seriously ill and everyone will go to hospital.

The Paper:In what season are these four pathogens prevalent?
Jin Dongyan:Generally speaking, it will be popular all year round, but it will be more serious in winter, especially in the northern region, which is also a known feature in the past.
The Paper:A doctor in Beijing was interviewed and mentioned that he has been engaged in pediatric diagnosis and treatment for more than 20 years. This time, the infection of Mycoplasma pneumoniae is the highest.
Jin Dongyan:In the post-epidemic era, when foreign influenza virus and syncytial virus broke out together with Covid-19, many doctors said that it looked more serious than ever. Is it actually worse? The answer is none.
You should look at the data of the whole city or the whole country. Up to now, there are not many places in China that have the conditions to do mycoplasma pneumoniae testing, and it may be impossible to test it at the district-level hospitals, and it is also inaccurate. How do you know if something happens to you? Plus mycoplasma pneumoniae infection is mostly asymptomatic. Without the test data of the past years, it is actually impossible to know whether this wave has the largest number of infected people.
From the weekly influenza report released by the National Influenza Center, it can be clearly seen that the number of cases with flu-like symptoms in northern China has increased significantly this year compared with the previous year, but it has not exceeded last year or 2017 and 2018 before the epidemic. Because mycoplasma pneumoniae infection can also cause flu-like symptoms, this statistic also reflects the prevalence and scale of mycoplasma pneumoniae to some extent. In short, it is not clear from this data that the number of people infected with mycoplasma pneumoniae is the highest this time.
Of course, due to the outbreak of mycoplasma pneumoniae in schools and kindergartens, a large number of patients go to the nearest hospital for medical treatment at the peak of the outbreak, which is really easy to cause heavy pressure on individual hospitals. Therefore, it should be understandable that pediatricians have this impression.
In fact, most patients who come to the hospital now are mild. So many people go to the hospital and it is easy to run on medical resources. Doctors are tired of coping and there is no way to give the best treatment.
And the disease is not difficult to treat, and it is not so special. If the doctor suspects that it is mycoplasma pneumonia, azithromycin has been used for 48-72 hours. If the fever has gone down, it will be right. If it doesn’t get better, it should be changed. Most international regulations suggest this, but it is not said that it must be tested first.
If testing must be done first, the capacity of testing must be increased, and the quality control and supervision of testing reagents must be in place. Moreover, the positive detection of nucleic acid must be combined with clinic or IgM antibody to make an accurate diagnosis. Many places in our country can’t do the first test, so there should be a clear procedure on how to diagnose and treat mycoplasma pneumonia.
It is necessary to classify diagnosis and treatment to avoid a run on big hospitals.
The Paper:According to media reports, the daily average number of patients in Beijing Children’s Hospital far exceeds the hospital’s carrying capacity. What do you think of the overload operation of the hospital?
Jin Dongyan:The main cluster epidemics of these four kinds of diseases occur in schools and kindergartens. Keeping an eye on schools and kindergartens can get twice the result with half the effort. Under the current situation, what we should do is to nip in the bud, find out early and take decisive measures when there is a small-scale cluster infection.
The risk of hospital overload operation is that increasing the gathering of these sick children in confined spaces will not only increase the risk of transmission, but also make it easier for people who really need treatment to be treated in time, and will also cause panic among the people.
The Paper:When do you expect this round of infection to peak?
Jin Dongyan:At present, we only see the sequence of pathogen detection rate, but we don’t see more data. We don’t know how big the infection scale is in Beijing, and we don’t know the data compared with the previous period or the past few years, so it is difficult to make an accurate prediction.
In fact, there are more than ten other pathogens that cause upper respiratory tract infection or community-acquired pneumonia. The data provided at present only say which ones have been detected, not which ones have not been detected or not. Generally, the proportion of community-acquired pneumonia with unknown causes is 50% or even higher. In winter, we should always be alert to community-acquired pneumonia caused by various reasons, and we should not take it lightly or worry too much.
According to the data released by the National Influenza Center, the peak of influenza should not have arrived yet.
According to the oral report of Beijing CDC, the number of children seeking medical treatment for mycoplasma pneumoniae infection has dropped from the peak, which may also indicate that this wave of mycoplasma pneumoniae infection has entered a downward period.
The Paper:Now, what can the public do?
Jin Dongyan:We should use common sense. Our child is ill, and the best care is to relieve his symptoms and then observe him closely. If your child’s body doesn’t show warning signs, don’t go to the hospital, because going to the hospital is easy to cause cluster infection, and most of them will be fine. If the illness is serious, or the child has basic diseases such as asthma, then he should go to the hospital as soon as possible.
The Paper:What symptoms do you need to go to the hospital in time? Is there a difference between adults and children in the standard of medical treatment?
Jin Dongyan:Children with persistent high fever for many days, persistent dyspnea (such as depression of intercostal muscles when breathing), wheezing, purple lips, low blood oxygen concentration, unconsciousness, aversion to water, original asthma and other basic diseases should see a doctor in any of the above cases.
Most healthy adults have experienced influenza or other upper respiratory tract infections, and there is little chance of developing pneumonia. Unless you have a basic disease, you need special attention.
From the family level, if children are ill, we should pay attention to isolation, especially not to let them contact the elderly, which is best for the elderly. If infected with the elderly, the old people’s original immunity is low, and they may be seriously ill or even life-threatening. The severe mortality rate of the elderly is relatively high, especially in nursing homes.
The Paper:At present, some parents take their children to the pediatric hospital, but the pediatric hospital is overloaded and the waiting time for treatment is generally long. When treating children’s respiratory tract infections, can we choose a general hospital with a shorter waiting time, and will there be any difference in treatment effect?
Jin Dongyan:It doesn’t make any difference. Because of these pathogens, only mycoplasma can use antibiotics such as azithromycin, and there are no specific drugs for other diseases, which are mainly symptomatic treatment. There are only a few kinds of drugs that doctors can choose.
After most infected people have symptoms, they will get better without taking antibiotics. The fever should be reduced, the cough should be stopped, and the allergy should be prevented. If there are any symptoms, symptomatic treatment should be given to alleviate the symptoms, pay attention to rest, and then go to school when you are completely better. The most important thing is not to touch the elderly.
The Paper:At present, we know that many community hospitals don’t have pediatrics, or don’t have the ability of initial diagnosis, so parents have to choose general hospitals or top three hospitals. What do you think of this situation?
Jin Dongyan:Common upper respiratory tract infection or pneumonia is not an incurable disease, and medical college graduates with medical training can effectively deal with it. It’s not that you have to find a pediatrician to cure it well.
The Paper:What is the self-limitation of these four pathogens now?
Jin Dongyan:After these four pathogens infect the respiratory tract, most of them are self-limiting and self-healing diseases. People susceptible to respiratory syncytial virus are also children, and adults are already immune, so children and the elderly are the most vulnerable groups. The susceptible population of mycoplasma is also children, especially school-age children, most of whom are infected when they gather at school.

The Paper:If there is mixed infection, what are the risks for patients?
Jin Dongyan:Mixed infections are rare. According to the data in the literature, only less than 10% of community-acquired pneumonia was found to have mixed infection. It is not easy to know whether it is a clinically significant mixed infection. Because many people are asymptomatic carriers of these pathogens. For example, asymptomatic carriers of mycoplasma pneumoniae are infected with adenovirus and cause pneumonia, but the results of mycoplasma nucleic acid are also positive. Whether it is mixed infection or not, which is the main cause, it is difficult to explain by the test results alone.
"Test before treatment" is not necessary.
The Paper:Some doctors said in an interview that drugs should be used only after the pathogen is determined. Is this correct?
Jin Dongyan:It is too idealistic and advanced to identify the pathogen first and then treat it, and even the most advanced areas in the world can’t do this. A few years ago, some regulations about mycoplasma pneumonia suggested this, but now they have all been returned. Because there are not so many reagents, and diagnosis is as good as no diagnosis. If pneumonia comes up, it is necessary to treat it quickly.
Our country can only complete these tests in large hospitals. Ordinary grass-roots hospitals and some large-scale hospitals do not have the ability to carry out routine tests, or they do not have the ability to carry out rapid tests on a large number of patients in a short period of time, and the quality control of most reagents provided now may not pass.
Secondly, in many cases, there is no need for pathogen diagnosis. If we insist that all people make pathogen diagnosis before treatment, it may delay the treatment of some critically ill patients.
In addition, not only these four pathogens can cause pneumonia now, but also more than a dozen pathogens can cause pneumonia, and there is more than half the chance that the pathogens can not be found at all by using existing means. If you must diagnose it, you may have to wait until he becomes seriously ill or can’t be saved. You can’t do this or wait. At the same time, this practice will cause a run on the resources of large hospitals, because we simply don’t have the ability to complete so many tests.
The Paper:From a scientific point of view, what are the specific detection methods for these four types of pathogens?
Jin Dongyan:Now basically rely on nucleic acid detection, but our ability of nucleic acid detection is limited, not infinite, and the production of reagents is limited, not infinite. There are many cases where nucleic acid is positive but completely asymptomatic or the symptoms are very mild. As far as mycoplasma pneumoniae infection is concerned, it is more reasonable to take nucleic acid and IgM antibody double positive as diagnostic criteria. According to international norms, outpatients generally do not do pathogen testing, and only inpatients do it.
The Paper:Uncertainty about the pathogen, is there a risk in treatment?
Jin Dongyan:According to the rules, it is necessary to prescribe antibiotics for trial treatment, and time is the most important thing.
Do you have a plan for the flu? No move. Do you have any ideas for other viruses? I didn’t say anything. Antibiotics are not necessary and should not be used for virus infection, but antibiotics should be tried immediately in an emergency when pneumonia occurs and the pathogen diagnosis is still unclear. You can barely use Tamiflu to find out the flu, but can Tamiflu be used frequently now? In fact, Tamiflu is only for people with special needs, and it can only be used at a high price. Not all people with flu have to eat or can eat Tamiflu. Now we can’t even hang up the date, and the monitoring cycle can’t be fast. When we find out the flu or COVID-19, we often miss the best administration time. Of course, if COVID-19 and influenza can be quickly identified or ruled out, it will be very helpful for clinical treatment. However, if we want to detect multiple pathogens separately, it may be time-consuming and laborious, but in the end it will have little effect. Doctors should try antibiotics decisively in combination with clinic and epidemiology, and make timely adjustments according to pathogen diagnosis and other test results.
Clinically, it is often more important to distinguish between viral infection and bacterial infection. Recent studies have shown that the level of procalcitonin in blood can be used for this purpose. This is actually more practical than detecting pathogens, and it has more clinical guiding significance. It is better to simply measure procalcitonin than to focus on detecting pathogens. If the level is low enough, antibiotics can be stopped as soon as possible in combination with clinical manifestations.
It is necessary to increase the proportion of vaccination for the elderly
The Paper:Azithromycin is a specific drug for mycoplasma pneumoniae. Is there any risk if parents give their children azithromycin by themselves?
Jin Dongyan:Of course there are risks. This is originally a prescription drug, and the world does not recommend giving antibiotics to children by themselves.
In addition, self-medication may delay the illness. For example, if the patient has the flu, the flu has developed to pneumonia, which is more serious. Give him antibiotics, and he will not be able to eat well, and the treatment of the flu will also be delayed.
The Paper:What is the efficacy of azithromycin in treating mycoplasma pneumonia? Some patients with mycoplasma pneumonia are resistant to azithromycin, will it affect their rehabilitation?
Jin Dongyan:Azithromycin is effective against mycoplasma. However, there are many mycoplasma pneumoniae resistant to azithromycin and other macrolide antibiotics in Asia, so it is not necessarily effective to detect azithromycin mycoplasma. In the final analysis, we should try to cross the river by feeling the stones. In case of azithromycin resistance, other antibiotics, including tetracycline and fluoroquinolones, should be used. However, children under 8 years old should not use tetracycline, and fluoroquinolones can still be used.
The most effective gold standard for judging azithromycin drug resistance is to use cultured mycoplasma for detection, but it is difficult and takes a long time. As mentioned above, it can also be used as a reference index according to whether the fever has gone down 48~72 hours after administration.
The Paper:Will there be repeated infections with these four pathogens?
Jin Dongyan:Could be a different pathogen infection. The first time may be adenovirus, the second time may be influenza, the third time may be Covid-19, and the fourth time may be something else. Unless the child’s own immunity is problematic, it is impossible to be infected with the same pathogen many times in a short period of time.
The Paper:Can the infection of four pathogens be prevented?
Jin Dongyan:As in COVID-19, keeping social distance, wearing masks as much as possible, washing hands frequently, etc., all return to the basic steps.
The Paper:Do these four pathogens have corresponding vaccines? How effective is it?
Jin Dongyan:Only the flu has a vaccine, and the other three pathogens have no vaccine. There is respiratory syncytial virus vaccine in the world, mainly for the elderly, but we haven’t approved it yet. Covid-19, Streptococcus pneumoniae and Haemophilus influenzae, which may also cause pneumonia, also have vaccines, and the elderly and children should be encouraged to actively vaccinate.
Influenza vaccine is quite effective, and the international standard is to give it to the elderly. Over the years, 60% of the elderly in Hong Kong have been vaccinated, and COVID-19 and influenza vaccines for the elderly and children are free or subsidized. The vaccination rate of the elderly in the mainland is low, which should be taken seriously.